Opyce Blog
Optimizing Reactive Energy Usage
Reactive energy is a term often overlooked, yet it plays a fundamental role in energy efficiency. Unlike active energy, which performs useful work, reactive energy does not directly perform work but is necessary to maintain the quality of electrical supply.
Inductive reactive energy appears in electrical installations, mainly when devices with coils are in operation. For example, any appliance that operates with a transformer, motors, compressors, ovens, fluorescent tubes, etc.
When electrical installations have an excess of reactive energy, higher generation and distribution capacity are required, leading to increased costs and energy loss in the system. To optimize the use of reactive energy, it is essential to use devices such as capacitors and filters to correct the power factor.
By improving the power factor, the amount of reactive energy required is reduced, enhancing the overall efficiency of the electrical system. This not only reduces costs but also eases the burden on the electrical grid, benefiting the environment.
Thus, proper management of reactive energy is key to maintaining an efficient and sustainable electrical network. By optimizing the power factor, companies can reduce operating costs and contribute to the conservation of energy resources.
Penalties for inductive reactive energy apply only to contracts with contracted power exceeding 15 kW in low voltage (tariff 3.0TD) and all contracts with high voltage, tariffs 6.1TD, 6.2TD, 6.3TD, and 6.4TD. The P6 period, corresponding to the time from 0 to 8 in the morning on weekdays, plus all weekends and state holidays, is exempt from this type of penalty.
The reactive energy billing term (€/kVArh) is defined by the power factor (cosφ), which measures the amount of reactive energy over the total energy and is calculated as follows:
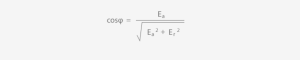
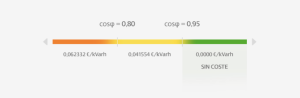
- If cosφ is greater than 0.95, no cost is applied.
- If cosφ is between 0.95 and 0.80, the cost is €0.041554/kVArh.
- If cosφ is less than 0.80, the cost is €0.62332/kVArh.
Capacitive Reactive Energy
Although not as common, capacitive reactive energy appears in electrical installations similarly to inductive reactive energy but with the opposite sign. It arises when the installation includes capacitor banks, LED lighting, computers, or buried cables.
Current law stipulates that penalties for capacitive reactive energy can only be applied to contracts with high voltage tariffs, specifically 6.1TD, 6.2TD, 6.3TD, and 6.4TD. If capacitive reactive energy in the installation exceeds 20% of the active energy consumed per hour, a penalty may be imposed. Currently, the CNMC proposes a price of €0 per each KVArh above the limit and leaves the door open for potential penalties later on.
Contact us, tell us how we can assist you, and we will be delighted to get in touch with you!